The current financial ecosystem is riddled with inefficiencies, lack of trust, and regulatory challenges.
Traditional finance (TradFi) struggles with high costs, manual processes, and limited innovation, while crypto based DeFi face issues of compliance, interoperability, and consumer protection.
Lack of compliance and oversight with the following undesirable consequences:
- Limited interoperability with traditional financial infrastructure
- Outright prohibition by many regulators around the world
- No consumer protection resulting in low trust levels among potential end-users
Traditional financial assets and services suffer from a number of structural challenges which make them sub-optimal in many ways
- Huge counter-party risk associated with custody
- Cumbersome and ineffective regulatory oversight
- High cost of human labor and associated brick and mortar infrastructure
- Delays, errors, and friction resulting from manual operation
- Impact of stringent but necessary controls on innovation
- Cost and time required to issue, store, move and process instruments

Challenges with Crypto
xLack of compliance and oversight with the following undesirable consequences:
- Limited interoperability with traditional financial infrastructure
- Outright prohibition by many regulators around the world
- No consumer protection resulting in low trust levels among potential end-users
Challenges with TradFi
xTraditional financial assets and services suffer from a number of structural challenges which make them sub-optimal in many ways
- Huge counter-party risk associated with custody
- Cumbersome and ineffective regulatory oversight
- High cost of human labor and associated brick and mortar infrastructure
- Delays, errors, and friction resulting from manual operation
- Impact of stringent but necessary controls on innovation
- Cost and time required to issue, store, move and process instruments
INTRODUCING REGULATED BLOCKCHAIN
Regulated blockchain leverages the programmability, transparency and immutability of blockchain to ensure that digital assets and applications are compliant and regulators have the required oversight.
Regulations are programmatic and compliance is enforced
Assets and instruments are represented in purely digital form
All instruments reside on-chain and do not require custody
Product and service operations are completely automated
Processes behind product functionality are audited and immutable
Complaint
xRegulations are programmatic and compliance is enforced
Paperless
xAssets and instruments are represented in purely digital form
Non - custodial
xAll instruments reside on-chain and do not require custody
Automated
xProduct and service operations are completely automated
Transparent
xProcesses behind product functionality are audited and immutable
Core Components
Regulated Blockchains are made up of four distinct layers each contributing to the smooth functioning of a simple and efficient value chain.
Core Infrastructure
Provides the ledger, runtime environment and other native functionality that facilitate the issuing of digital assets and delivery of financial apps
Regulatory Applications
Provides programmatic rules and enforcement mechanism to constrain the behaviors of assets, applications and service providers
Product Ecosystem
Consists of the digital assets and apps built by various service providers to address diverse needs of end-users
End-User Interfaces
Consists of third party applications through which individuals and organizations consume financial services offered on Regulated Blockchains
Core Infrastructure
The Core Infrastructure of Regulated Blockchains provides the foundational layer for secure, compliant, and efficient financial services
Network Nodes are licensed by relevant regulators within each applicable jurisdiction.
- Nodes -Are hosted by regulators and regulated institutions.
- Connectivity Is via a virtual private network.
- Consensus is based on proof of authority protocol.
A decentralized and synchronized transaction database that ensures transparency, immutability, and real-time updates across all participating nodes.
A fee structure that balances commercial and non-commercial validators, prioritizing cost efficiency while incentivizing network developers and administrators
Validator and archival nodes that maintain ledger integrity, verify transactions, and enhance network security by preventing unauthorized modifications
Cryptographic techniques and anonymization protocols safeguard transactions, ensure data integrity, and provide regulators with controlled visibility
A Proof of Regulation (PoR) model where only licensed financial institutions operate validator nodes, ensuring compliance and deterring fraudulent activity
PA distributed execution environment that runs smart contracts securely and tamper-proof, ensuring compliance and consistency in financial operations
Economics
xA fee structure that balances commercial and non-commercial validators, prioritizing cost efficiency while incentivizing network developers and administrators
Shared Ledger
xA decentralized and synchronized transaction database that ensures transparency, immutability, and real-time updates across all participating nodes.
Network Nodes
xValidator and archival nodes that maintain ledger integrity, verify transactions, and enhance network security by preventing unauthorized modifications
Nodes Connectivity
xNetwork Nodes are licensed by relevant regulators within each applicable jurisdiction.
- Nodes -Are hosted by regulators and regulated institutions.
- Connectivity Is via a virtual private network.
- Consensus is based on proof of authority protocol.
Security and Privacy
xCryptographic techniques and anonymization protocols safeguard transactions, ensure data integrity, and provide regulators with controlled visibility
Consensus Algorithm
xA Proof of Regulation (PoR) model where only licensed financial institutions operate validator nodes, ensuring compliance and deterring fraudulent activity
Application Run-Time
xA distributed execution environment that runs smart contracts securely and tamper-proof, ensuring compliance and consistency in financial operations
PRODUCT ECOSYSTEM
The Product Layer enables the creation, automation, and self-custody of digital financial products on Regulated Blockchain
PRODUCT ECOSYSTEM
The Product Layer enables the creation, automation, and self-custody of digital financial products on Regulated Blockchain
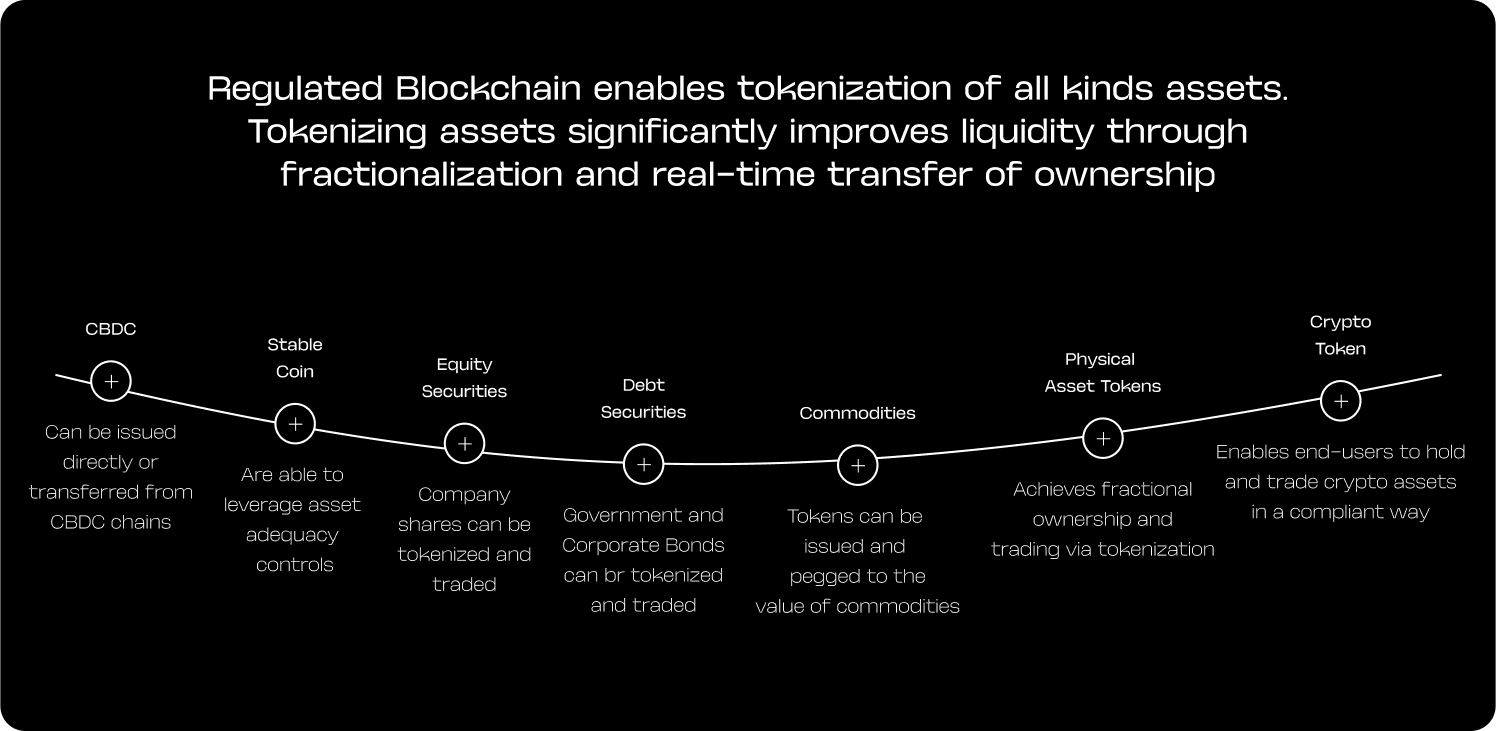
Regulated Blockchain enables tokenization of all kinds assets. Tokenizing assets significantly improves liquidity through fractionalization and real-time transfer of ownership
CBDC
Can be issued directly or transferred from CBDC chains
Stable Coin
Are able to leverage asset adequacy controls
Equity Securities
Company shares can be tokenized and traded
Debt Securities
Government and Corporate Bonds can be tokenized and traded
Commodities
Tokens can be issued and pegged to the value of commodities
Physical Asset Tokens
Achieves fractional ownership and rading via tokenization
Crypto Tokens
Enables end-users to hold and trade crypto assets in a compliant way
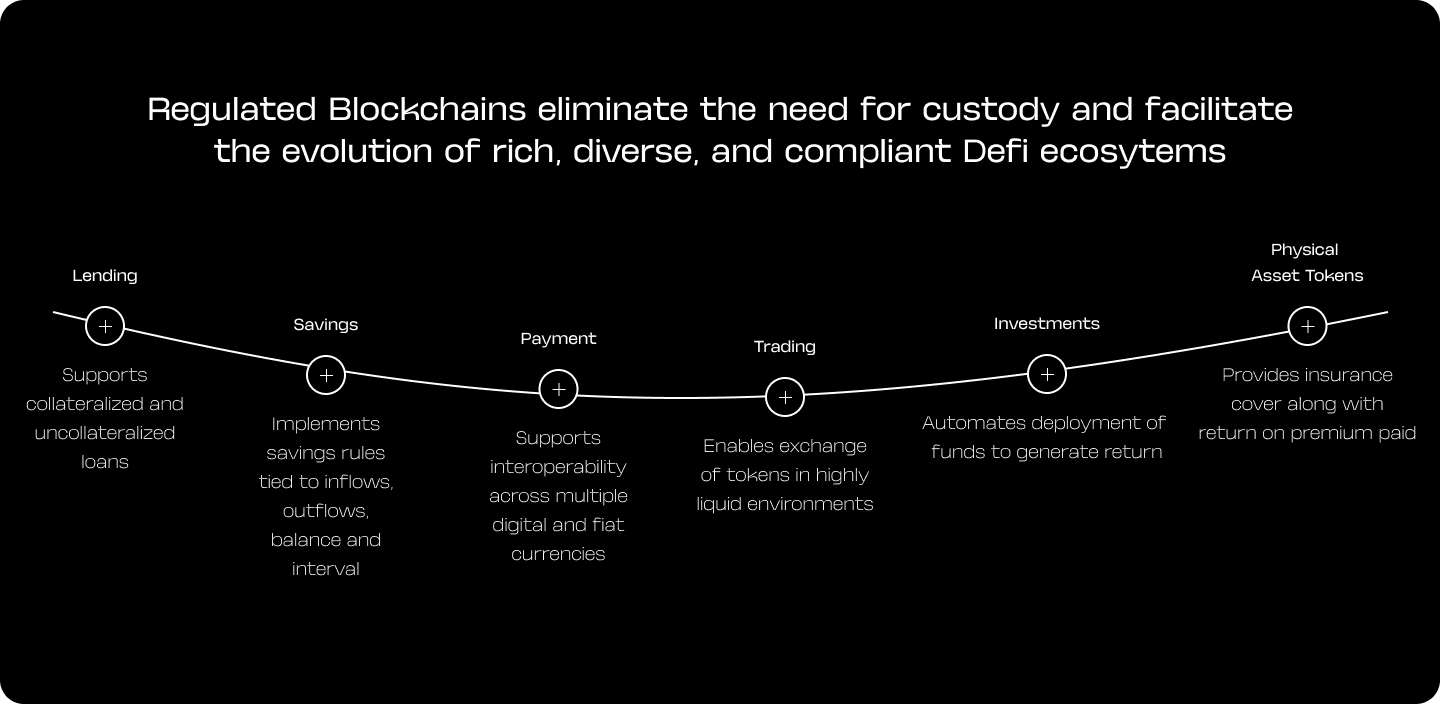
Regulated Blockchains eliminate the need for custody and facilitate the evolution of rich, diverse, and compliant Defi ecosytems
Lending
Supports collateralized and uncollateralized loans
Savings
Supports collateralized and uncollateralized loans
Payment
Supports collateralized and uncollateralized loans
Trading
Supports collateralized and uncollateralized loans
Investment
Supports collateralized and uncollateralized loans
Physical Asset Tokens
Supports collateralized and uncollateralized loans
EXTERNAL INTERFACE
The External Interface layer Provides Seamless access to Regulated Blockchains through Graphic, Agentic, and Embedded Interfaces
Regulated Blockchain is designed to integrate effortlessly into the digital financial ecosystem, offering multiple ways for users to interact. Whether through menu-based interfaces, Agentic AI assistants, or embedded into enterprise financial applications, it ensures accessibility and usability across various channels. End-user interface providers deliver off-chain functionality that connects users to on-chain assets and services, enabling seamless interaction between Regulated Blockchains and the real-world.
Wallet Application
PFM Application
Payment Terminals
Payment Gateways
Financial Management Platforms
REGULATORY APPLICATION
Regulated Blockchains take advantage of blockchain’s characteristics to automate regulation. The regulatory applications layer within regulated blockchains applies three (3) main principles to achieve effective regulation of digital assets and financial services
Token templating ensures that digital assets are compliant by requiring issuers to use pre-built token issuance services that cater for all compliance requirements including
- KYC Assurance
Enforces submission of ID and implements restrictions based on KYC levels. - AML Screening
Enforces AML screening and suspected transaction reporting. - Custom Screening
Ensures that only transactions that have been screened, can effect a transfer of value.
- Transaction Parameter Validation Regulatory programmes validate actual transaction parameters against expected parameters as determined by predefined rules
- External Parameter Validation Regulatory programmes validate actual external records linked to each transaction against the expectation of what such records should be as determined by predefined rules
Regulated blockchain requires automated code screening and audits each time a new application or new version of an application is deployed.
- Compliance Screening
Confirms that the code base is compliant with relevant regulatory coding conventions. - Security Screening
Confirms that the code base does not contain fraudulent logic or malicious code snippets - Custom Screening
Ensures that only transactions that have been screened, can effect a transfer of value.
Token Templating
xToken templating ensures that digital assets are compliant by requiring issuers to use pre-built token issuance services that cater for all compliance requirements including
- KYC Assurance
Enforces submission of ID and implements restrictions based on KYC levels. - AML Screening
Enforces AML screening and suspected transaction reporting. - Custom Screening
Ensures that only transactions that have been screened, can effect a transfer of value.
Transaction Screening
x- Transaction Parameter Validation Regulatory programmes validate actual transaction parameters against expected parameters as determined by predefined rules
- External Parameter Validation Regulatory programmes validate actual external records linked to each transaction against the expectation of what such records should be as determined by predefined rules
Application Screening
xRegulated blockchain requires automated code screening and audits each time a new application or new version of an application is deployed.
- Compliance Screening
Confirms that the code base is compliant with relevant regulatory coding conventions. - Security Screening
Confirms that the code base does not contain fraudulent logic or malicious code snippets - Custom Screening
Ensures that only transactions that have been screened, can effect a transfer of value.
Regulated Blockchains are a radical departure from both crypto and TradFi yet, incorporate the best of both worlds and hold the key to unlock a golden age of financial services across the globe

Obi Emetarom